Why MountainTrue Must Fight Racism
Why MountainTrue Must Fight Racism
When MountainTrue was formed through the merger of the Western North Carolina Alliance, the Environmental Conservation Organization and the Jackson-Macon Conservation Alliance in 2015, the organization inherited a broad scope of programs focused on protecting our rivers and public forests, reducing our region’s dependence on fossil fuels and encouraging smart growth to improve the health of our communities and reduce the impacts of development on our natural environment.
In the five years since the merger, the organization has been working on addressing issues of racism and equity: all MountainTrue staff members enroll in the Racial Equity Institute, the Building Bridges program or both; we’ve taken strides to diversify our board and staff; and we’re working to build partnerships with communities that are fighting for equitable access to resources and power.
That process has been coalescing and transformational. If you had asked us five years ago, two years ago or even just a few weeks back about our priorities and responsibilities on race and equity, you would have gotten different answers than today. We’ve been evolving toward a wider focus. Yes to protecting forests and rivers and advocating for better public transit, more greenways, clean energy, and dense development for the environmental benefits, but we are also thinking more broadly about how we can help foster communities where people are truly healthy. And this means communities that are free from racism, and where there is equity in the social determinants of health — housing, transportation, education and jobs.
Racial segregation and poverty are outcomes of bad policy.
Poverty and racial disparities have been sustained through bad policies that have disproportionately impacted people of color. This is clearly evident in the histories of Redlining and Urban Renewal. Redlining was the systemic denial of services, especially home loans, to people in Black communities established by the Federal Housing Administration in 1934 and replicated by private lenders and local governments that established racially-restrictive local zoning ordinances. Through a combination of redlining, deed restrictions, exclusionary zoning and leasing practices, and racism on the part of local governments, Black people were relegated to the poorest neighborhoods with the least public services. And because Black people could not get loans to improve or fix their homes, the quality of housing and other structures in these neighborhoods deteriorated and property values fell such that homeownership for Black families did not allow for the accumulation of generational wealth.
Despite these restrictions, Black communities in Asheville like Hill Street and Stumptown, the East End and the South Side were vibrant, thriving centers of Black life. City planners, however, saw only pockets of urban decay ripe for redevelopment under the guise of “Urban Renewal.” In the years after World War II, the federal government funded a massive building boom through the passage of the Housing Acts of 1949 and 1954, and the construction of a vast network of highways through the Federal Highway Act of 1944. With federal dollars flowing to municipal coffers, cities like Asheville were free to redevelop their urban cores, and it was poorer Black neighborhoods that were targeted. Much of the East End was razed to make way for South Charlotte Street and MLK Drive. In the Southside neighborhood more than 1,000 homes, 50 businesses and seven churches were demolished to make way for more upscale housing. In the Hill Street neighborhood, entire street grids were erased from the map to make way for Asheville’s Cross-Town Expressway.
In towns and cities across the country, vibrant communities of color were destroyed and their residents displaced. Some were forced to live in public housing communities that became pockets of concentrated poverty. Many others had to find cheap housing in the least desirable areas near highways, factories, refineries and landfills.
A View of Eagle Street
A view of Eagle Street looking east from the intersection with Biltmore Ave. This was the vibrant business center of the historically African American East End neighborhood. Photo by Warren Guggeheim circa 1950, courtesy of North Carolina Collection, Pack Memorial Public Library, Asheville, North Carolina.
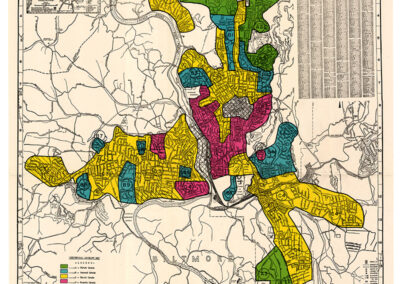
HOLC Map of Asheville
After the Great Depression, the U.S. government’s Home Owners’ Loan Corporation set out to evaluate the riskiness of mortgages. Their infamous redlining maps are a portrait of the racism and discrimination that has shaped American housing policy. Source: the Mapping Inequality project at the University of Richmond. https://dsl.richmond.edu/
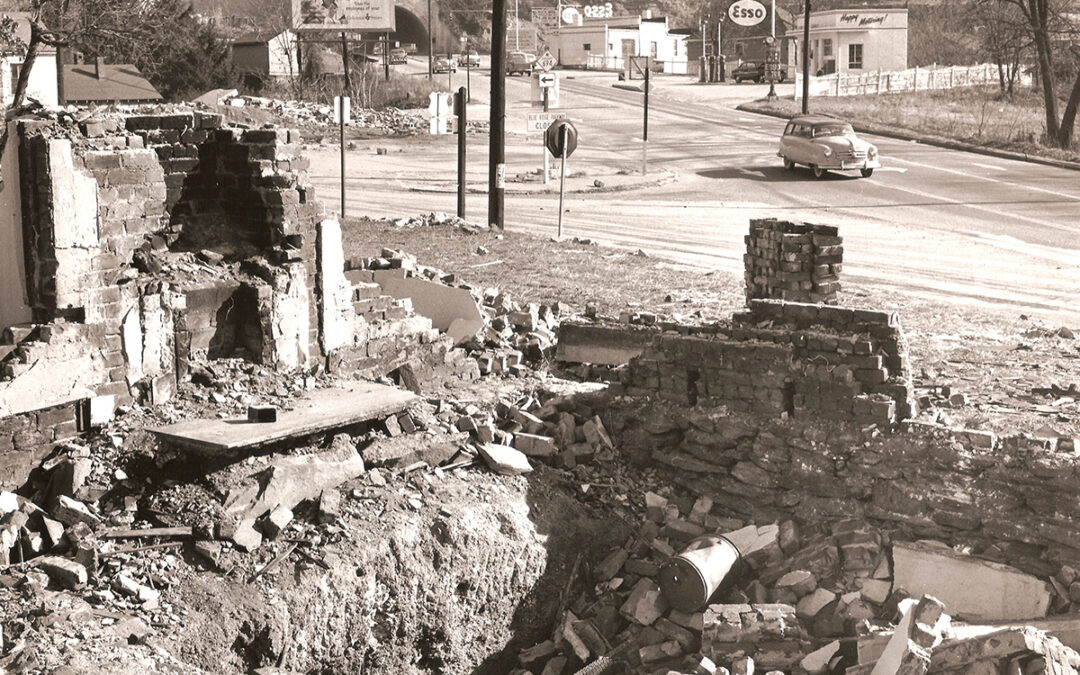
Displacement for Crosstown Expressway
This photo from Dec. 29, 1958, shows the demolition of buildings for the construction of the Asheville Crosstown Expressway. Asheville Crosstown Expressway. © Asheville Citizen Times via Imagn Content Services, LLC
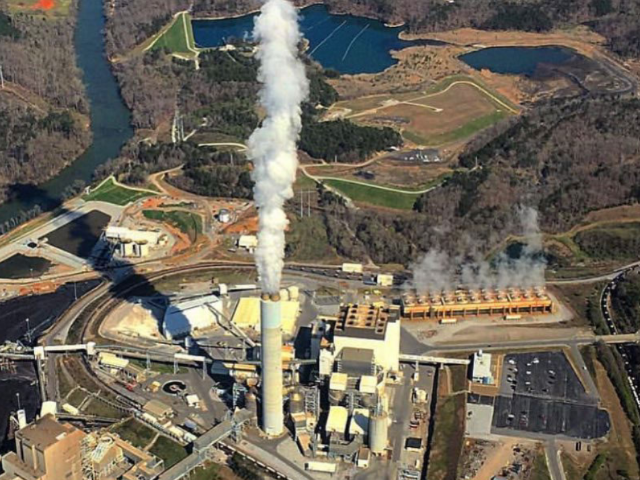
Pollution disproportionately affects the poor and communities of color.
These neighborhoods where the air is thicker with automobile exhaust, smog and fumes, and the soil and water are more likely to be poisoned with lead, heavy metals and other industrial pollutants have been dubbed “sacrifice zones.” The higher concentrations of pollution in these areas have an enormous effect on human health and childhood development and perpetuate the cycle of poverty. For instance, generations of poor kids who grew up near highways breathed air thick with the exhaust of leaded gasoline, and, even now, children in these neighborhoods are more likely to have high blood lead levels because the soil near these roads is still contaminated. Lead has been linked to reduced IQs, attention problems and aggressive behavior, and has been identified as a possible cause of the crimewave that besieged the nation from the mid-sixties through the early nineties.
It would be a mistake to reduce this oppression to simply matters of historical mistakes, market demand and geography. Redlining was explicitly racist, as was the targeting for destruction of poor and communities of color by mid-twentieth century urban planners. Similarly, proximity does not fully explain why Black and Brown communities suffer higher levels of air pollution. The National Center for Environmental Assessment finds that Black and Latino people are exposed to about 1.5 times and 1.3 times more particulate matter, respectively, than White people and that emissions are generally higher from factories located in communities of color than those located in wealthier White neighborhoods. Decisions are being made to site more polluting factories in poor neighborhoods than rich neighborhoods, and then to run the factories in Black and Brown neighborhoods dirtier. This is more than economic oppression. It’s environmental racism and it’s a dynamic that has been repeated time and again — famously in the financial decisions that lead to the Flint, Michigan water crisis and the state’s negligent response. Poor people are exploited for profit, and Black and Brown people most of all.
No zone should be sacrificed.
The society that we now inhabit is one where Black and Brown people have fewer opportunities, are more likely to live in areas that are polluted and dangerous, and are more likely to be trapped in cycles of poverty. To make matters worse: layered on top of this structural racism is a brutal criminal justice system, a broken healthcare system, an anemic educational system, crumbling infrastructure and growing food insecurity. In each and every regard, the consequences of these systemic failures fall heaviest on poor Black, Indigenous, and people of color.
Set to topple all these fragile civic institutions is the leviathan threat of Climate Change, which, if left unchecked, will flood our lowlands and mountain valleys in wet years and burn our mountaintops in drought years. Already, the outlines of this dystopia are clear: people and communities with resources will be better positioned to adapt, fortify and recover from disasters. Poorer communities will be sacrificed, largely abandoned by our federal government like New Orleans after Hurricane Katrina, the American citizens of Puerto Rico after Hurricane Maria, the Black neighborhoods of Houston that were flooded by industrial pollution during Hurricane Harvey, or the towns in Eastern North Carolina where homes were flooded with water tainted by millions of gallons of animal waste during Hurricane Florence.
But acting on climate change is not simply altruism, because the security of wealth will be fleeting. Climate Change is proceeding at a pace that has taken scientists by surprise and contributes to a wide spectrum of related maladies such as water shortages, crop destruction and the spread of diseases such as COVID-19. The climate challenges laid out in the October 2018 IPCC report will be insurmountable for a nation that is depleted and divided. Time is running out: to avoid climate catastrophe, we must stop sacrificing our most vulnerable populations, unite and act now.
Aftermath of Hurricane Sandy
Hurricane Sandy ravaged large portions of the Northeastern United States, damaging homes in poor, working class and wealthy communities, illustrating that no one is immune from the effects of climate change. Photo Courtesy of Marine Expeditionary Force by Cpl. Bryan Nygaard. (2012)
Our conscience demands action and unity.
The wider movement needed to repair our country, protect our environment and take on climate change must be multicultural and firmly committed to dismantling racism and all systems of structural oppression. This was the strategic rationale of Martin Luther King’s Poor People’s Campaign — which he described as “the beginning of a new co-operation, understanding, and a determination by poor people of all colors and backgrounds to assert and win their right to a decent life and respect for their culture and dignity” — and later of Jesse Jackson’s Rainbow Coalition. Both civil rights leaders understood that an anti-racist movement in which White participation is based only on notions of altruism of charity will exhaust itself and fail to create the mass politics needed to win lasting systemic change.
It’s been two years since the 2018 IPCC report was published warning of dire circumstances of not taking bold, swift action to curtail climate catastrophe. It has been nearly 40 years since Professor and NASA scientist James Hansen gave Congressional testimony about the threat of global warming. In that time our elected leaders have failed to meet the challenge head on. Worse, they’ve scoffed at proposals of the magnitude needed to address the climate crisis head on.
We have our work cut out for us. MountainTrue and its members must commit to the work of dismantling structural racism and uniting our communities in the fight for justice and survival in the face of climate change. Neither cause can succeed on its own; all are interconnected. We know that we don’t have all the answers, but we’re ready to stand shoulder to shoulder with communities fighting for justice.
As an organization, MountainTrue is committed to fighting racism and economic inequity, because meeting our core mission of protecting communities and the environment requires it. This means we must be ready to take on fights that are beyond the scope of traditional environmentalism. We will live our values and use our influence and institutional power to win a more equitable future, and we invite you, as a MountainTrue supporter, to join us.