Protect the Nolichucky River! Tell NC DEQ: Require Stronger Environmental Protections for CSX’s Railroad Rebuild
Protect the Nolichucky River! Tell NC DEQ: Require Stronger Environmental Protections for CSX’s Railroad Rebuild
Photo courtesy of Jubal Roe.
Keep advocating to protect the Nolichucky! Please comment now to ensure stronger environmental requirements for CSX as they rebuild their railroad through North Carolina’s Nolichucky River Gorge.
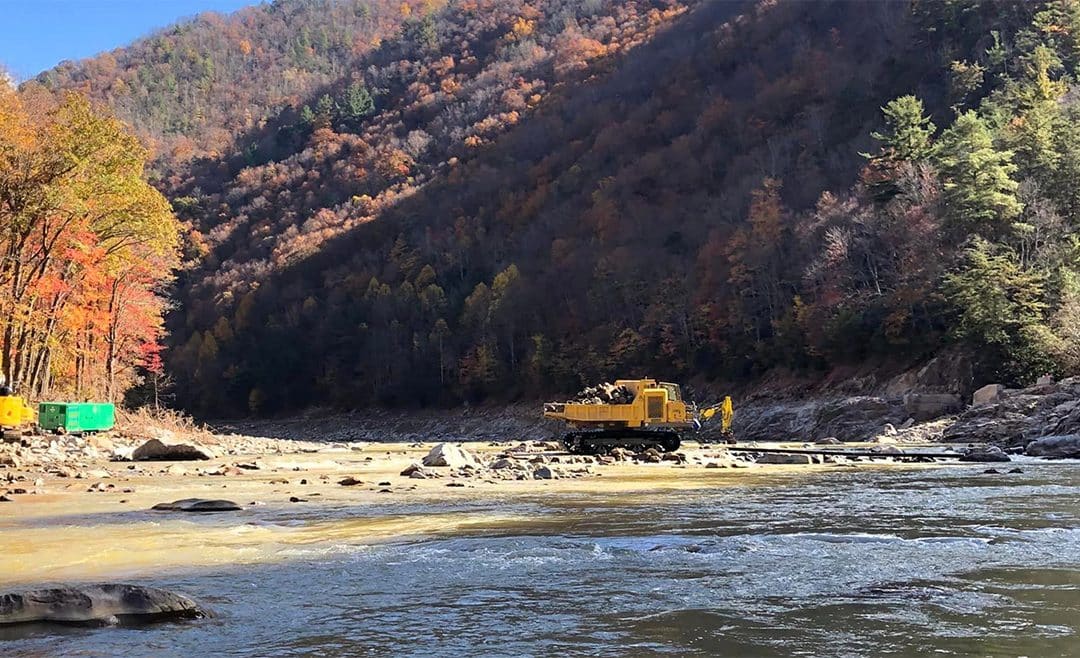
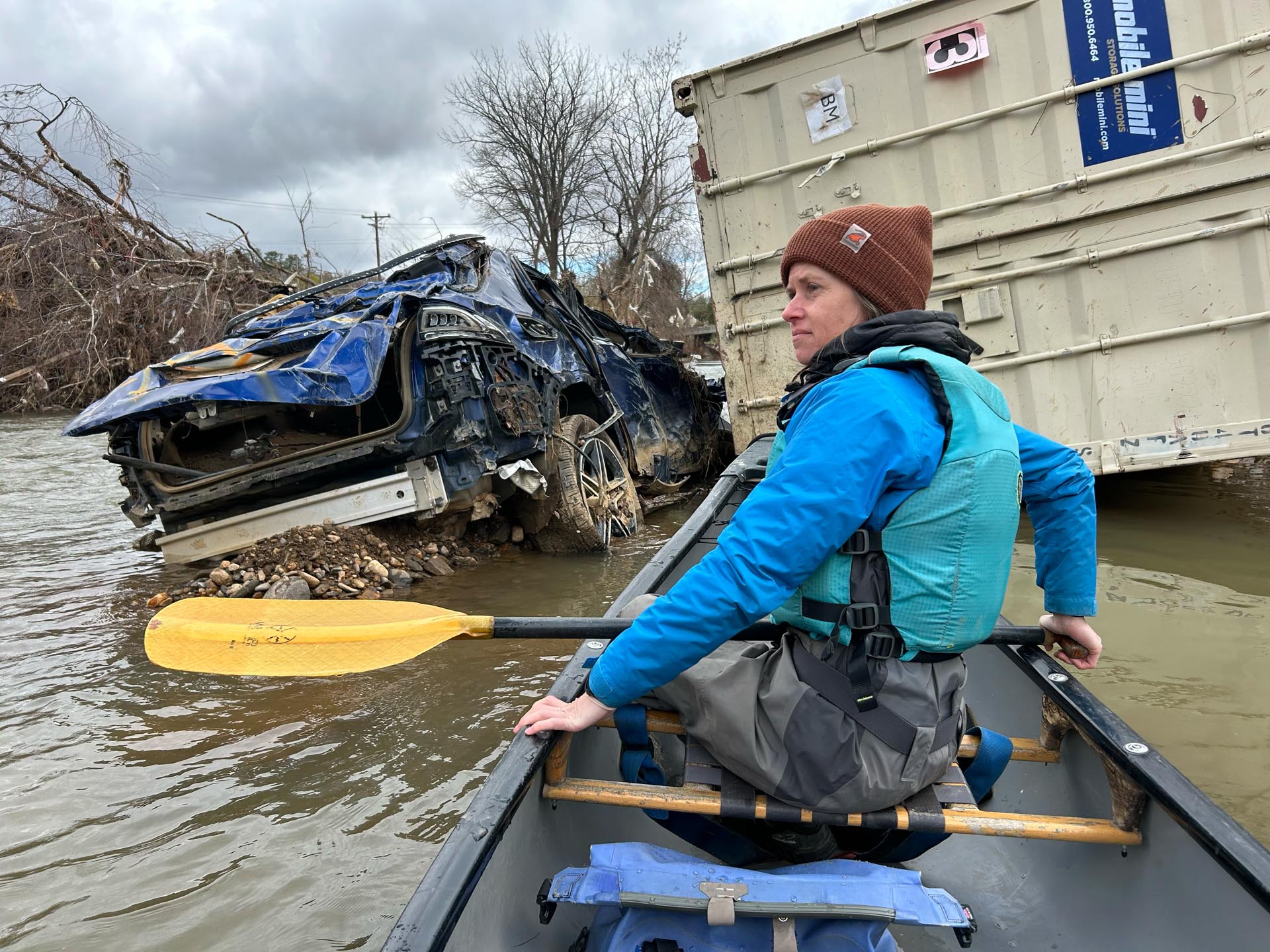
North Carolina’s Department of Environmental Quality is requesting public comment on CSX’s application to rebuild their railroad through our state’s section of the Nolichucky River Gorge. You may recall that CSX’s railroad experienced extensive damage as a result of Hurricane Helene, and CSX immediately started rebuilding in a manner that was highly damaging to the Nolichucky River’s Wild and Scenic values. Your advocacy helped stop their destruction previously but unfortunately, CSX is back at it under new approvals from the Army Corps of Engineers.
The North Carolina Department of Environmental Quality can stop CSX’s most harmful practices and we need your help again pushing for strong environmental protections in their permit. Please use the link below to submit comments and help us protect the Nolichucky. We encourage you to make your comment your own, but the following may serve as a framework:
https://edocs.deq.nc.gov/Forms/401_Public_Notice_Comments
ID#: 20241562
Version: 2
Project Name: CSXT Emergency Track Rebuild Post Hurricane Helene
Your stance on the project: No
Comment:
I am opposed to this project without additional protections. The following provisions, if included, would allow me to support this project:
- DEQ should prohibit any harvesting, mining, or excavation of material from below the ordinary high-water mark. Tennessee’s Department of Environment and Conservation has already prohibited the removal of material below the ordinary high-water mark in Tennessee. NC DEQ should do the same.
- DEQ should establish an ordinary high-water mark using the Army Corps’ January 2025 Ordinary High-Water Mark Manual. That analysis indicates the ordinary high-water mark should be approximately 6 feet above baseflow in the Gorge.
- DEQ must prohibit the removal of rock or any other material from any named rapid.
- DEQ should require CSX to provide for safe recreational and commercial whitewater access during reconstruction.
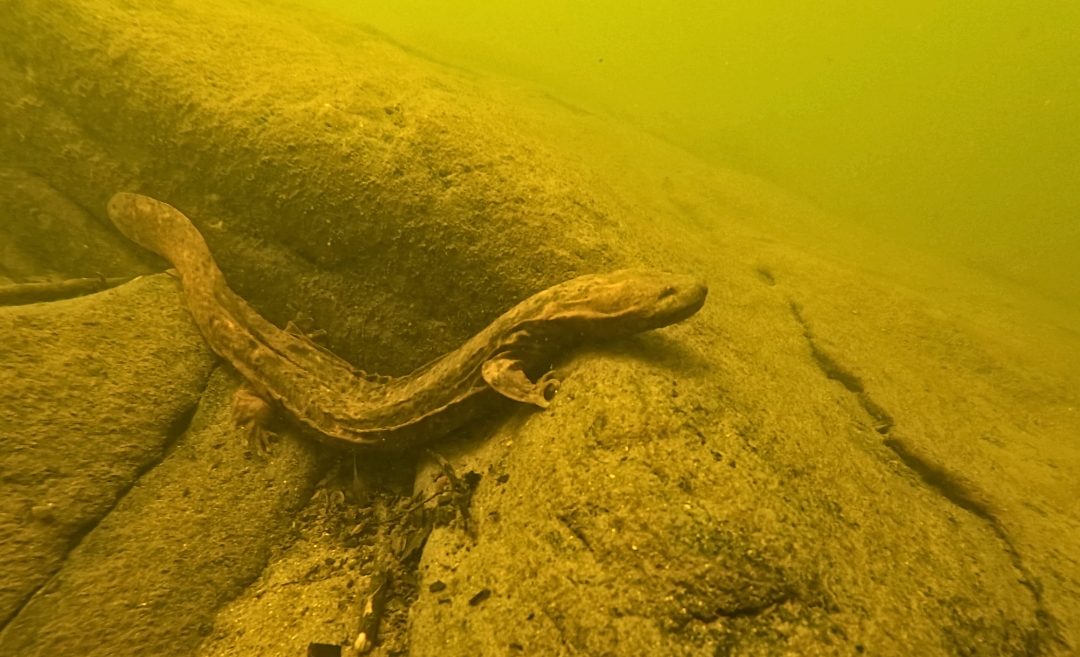
- The Nolichucky Gorge has been designated by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service as critical habitat for the endangered Appalachian Elktoe. It is also habitat for the Eastern Hellbender, which the Fish and Wildlife Service recently proposed for listing under the Endangered Species Act. DEQ should require CSX to survey areas for Appalachian Elktoe and Eastern Hellbender presence before CSX takes any action – including operating machinery such as dump trucks and excavators – below the ordinary high-water mark.