MT Raleigh Report: Politics, Disaster Relief, and the Fight for Western North Carolina’s Future
MT Raleigh Report: Politics, Disaster Relief, and the Fight for Western North Carolina’s Future
What a year – in Raleigh and, of course, in Western North Carolina.
Among the many lessons those of us here in the mountains learned, again, this year is that what happens – or does not – in Raleigh has a real impact on our communities, our mountains, and our future.
Certainly, that has to be one of the takeaways about the North Carolina General Assembly’s response to the disaster that hit the mountains a couple of months ago. Since September, the legislature has approved three bills that included disaster-related funding for a total of $1.13 billion in state funds. Click here for an overview of the legislature’s efforts on the disaster to date.
The most recent of these bills is SB382, which included $225 million transferred to a state fund for disaster relief but NOT approved for any specific program or project. Leaving that transfer aside, SB382 included a mere $32 million approved for disaster relief. The remaining balance must be earmarked and approved by the legislature before it reaches WNC.
Beyond the first dozen or so pages loosely focused around disaster relief are over 100 pages of “Various Law Changes,” the real meat of SB382 designed largely to shift power away from the executive branch. This power grab disguised as disaster relief caused three WNC Republican Representatives – Mike Clampitt, Karl Gillespie, and Mark Pless – to join Democrats in voting against the bill, although it passed both the House and Senate in otherwise party-line votes. It also prompted Governor Cooper to veto the bill, but his veto was later overridden by Republican supermajorities in both chambers and became law. Despite their initial opposition to the bill, Clampitt, Gillespie, and Pless all voted to override the veto and allow the bill to become law.
So why is disaster relief getting held up? It’s certainly not because money’s tight. State Budget officials recently told a legislative committee has a whopping $9.1 billion in inappropriate reserves, including almost $4.8 billion that was in the state’s “rainy day fund” itself when Helene hit, plus $1 billion in a stabilization and inflation reserve and another $732.5 million in a emergency response/disaster reserve. Legislators could also use another $1.1 billion from savings and still remain in compliance with state law.
Gov. Cooper’s request for a $3.9 billion state set-aside for hurricane relief presumed the use of about $3.5 billion from these sources.
So, if money is not the problem, what is the hold up on state disaster relief? For their part, budget writers for the Republican majorities in the House and Senate argue that it’s smart policy to hold back state relief funding and allow federal disaster relief to make its way to the region. They worry that if state funds are used on efforts that are eligible for federal relief, the feds may not reimburse the state for its recovery efforts. GOP budget writers say it’s better to let the federal money be the first in – and the state funding the last to address needs FEMA and other federal programs do not get to. They also point out that Congress is likely to provide more money for WNC recovery before the end of 2024.
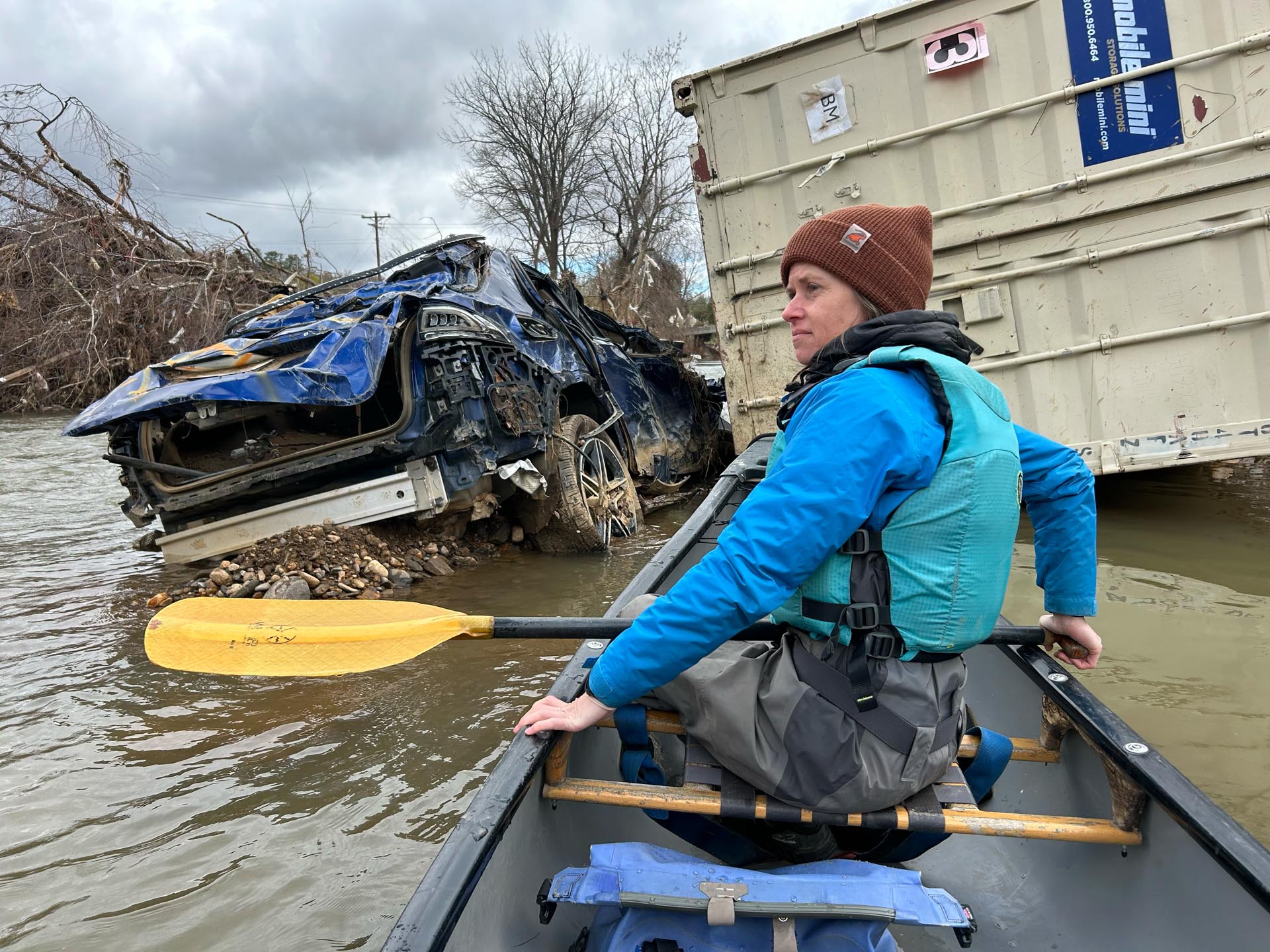
The problem with waiting, of course, is that many in WNC need help, now, for things we know that the federal government won’t pay for. Many small business owners, for example, can’t afford to take on more debt via the disaster loan programs offered by FEMA. Without direct grants, many business owners say their businesses won’t survive the disaster.
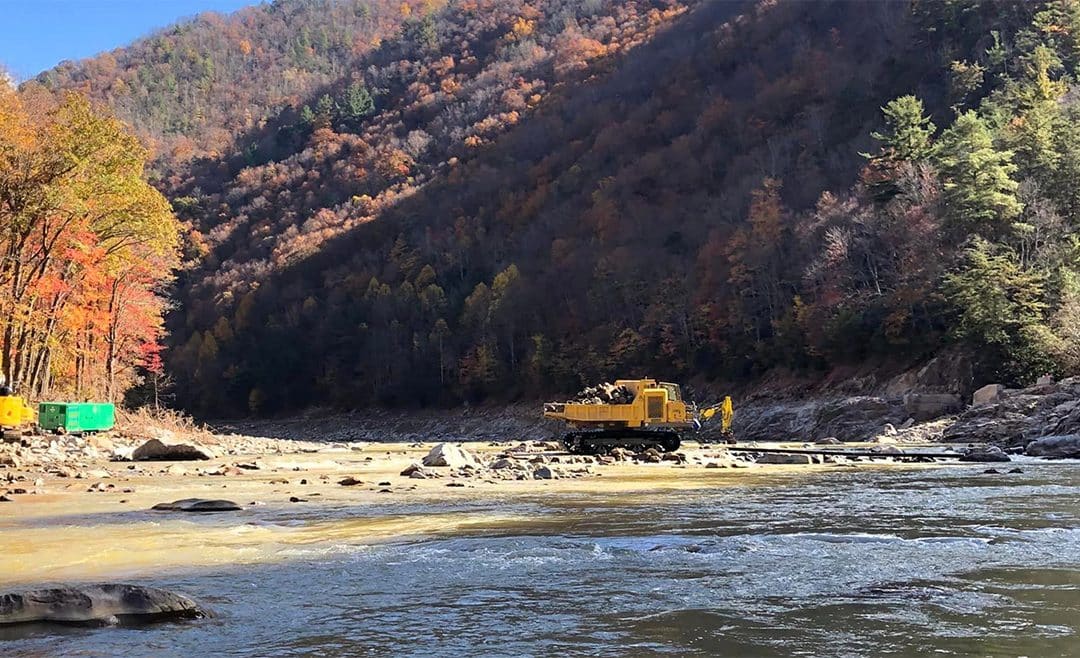
Debris removal is also an urgent need. While the federal agencies and the North Carolina Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services have both state and federal funds to help local governments clear rivers of storm debris, these funds are often restricted to trees and other natural debris – not the cars, trucks, and tons of garbage that were swept into every river basin in the region – and are further restricted to those debris jams that pose a risk to flooding or structural damage. The funding is also distributed locally, making regional clean-up efforts more difficult to get up and running. And timing is important: our rivers and streams need to be safe and ready to use come spring when the outdoor recreational season brings thousands of visitors and their dollars to the region.
With those waters – and our outdoor economy – in mind, MountainTrue has asked legislators to fund a regional debris clean-up effort that is also supported by the outdoor recreation industry’s umbrella group, the Outdoor Recreation Coalition. Our goal is to employ those in the outdoor industry, who have been displaced by the disaster, to clear out tons of debris in time for the start of the recreation season this spring. Despite the legislature’s reluctance to use state funds for this kind of effort, MountainTrue has started a small pilot program in Madison County with private funds that will make some popular whitewater safe for paddlers early in 2025.
We plan to use this pilot to continue to lobby legislators for debris removal funding – and employment for those put out of work by the disaster. Early word in Raleigh is that legislators will take up a state-funded package of disaster recovery efforts early in their 2025 session, which begins in late January.
Looking further back into the legislature’s work this year doesn’t provide much more to celebrate. With GOP supermajorities in both the House and Senate AND a budget surplus topping $1 billion, legislative leaders were unable to muster the votes to send a revised budget for FY2024-2025 to Gov Cooper this summer. In the absence of a revised budget, they left the surplus uninvested and dozens of important conservation projects, including many in WNC, unfunded.
Unfortunately, the 2025 legislative session doesn’t provide much hope that lawmakers will address the many issues facing North Carolina. With the GOP supermajority now gone in the House, the 2025 session promises to be a drawn-out stalemate between the GOP leadership in the General Assembly and Governor-elect Josh Stein, a Democrat.
For its part, MountainTrue will continue to be in the middle of debates about disaster recovery and rebuilding, clean water and air, and sustainable development and rebuilding. Thank you for the investments you make in MountainTrue and its work in Raleigh – we couldn’t do it without you.