One Million Gallons of Sewage Overflowed into Western North Carolina Waterways during Six Month Period
One Million Gallons of Sewage Overflowed into Western North Carolina Waterways during Six Month Period
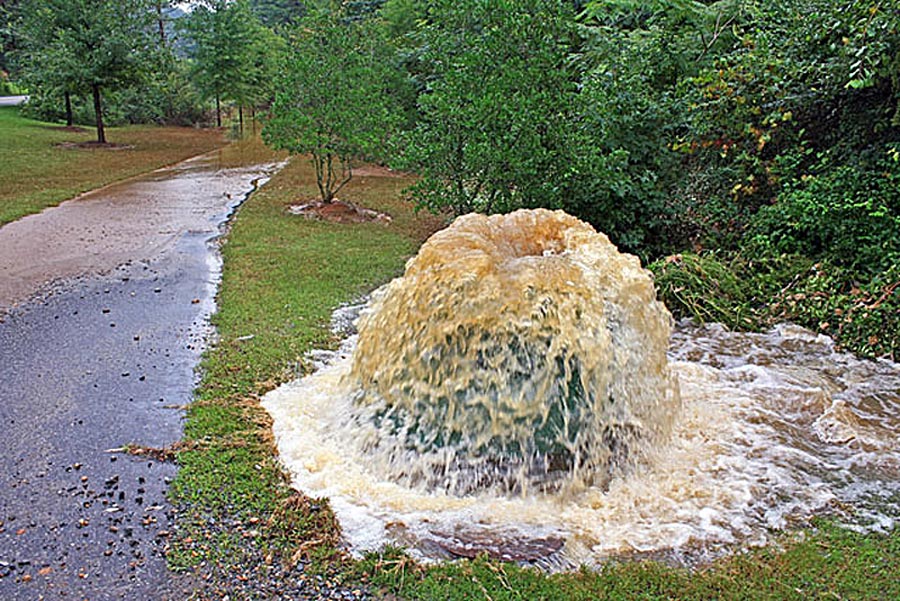
Photo credit: Alan Cressler, USGS. Public domain.
Asheville, NC — More than one million gallons of sewage overflowed from inadequate wastewater infrastructure into the French Broad River and other area waterways in Western North Carolina according to state data acquired and analyzed by MountainTrue. The data was collected from August 3, 2020 until March 4, 2021 by the North Carolina Department of Environmental Quality’s (DEQ) Asheville Regional office and is the best available estimate of the amount of sewage that overflows from wastewater infrastructures such as pipes and manhole covers into area rivers and streams across 19 counties of western North Carolina.
TAKE ACTION TO FIGHT E. COLI POLLUTION IN OUR RIVERS
We know the sources of E. coli pollution. Now we have the solutions to clean up our rivers. Advocated for major investments in wastewater infrastructure, and stand up for science-based policies to help farmers fence cattle out of streams and property owners fix their septic systems.
MountainTrue, a local conservation organization, monitors water quality throughout Western North Carolina and in Union and Towns counties in North Georgia for pollution, including levels of E. coli — an indicator of the presence of bacteria and other pathogens that are harmful to human health. The organization has documented a dramatic increase in bacteria pollution of the French Broad River Watershed over the past two years and concerning trends in other area watersheds.
“What we have seen over the past few years has me worried about the future of river recreation on the French Broad River,” explains Hartwell Carson, MountainTrue’s French Broad Riverkeeper. “Take Pearson Bridge in Asheville’s River Arts District: That site passed the EPA’s safe threshold for swimming 81% of the time in 2016. Then in 2020, that site failed 81% of the time. Or Mud Creek in Henderson County, that site used to be safe at least 50% of the time and now it fails 93% of our tests.”
In April, MountainTrue released results from DNA testing that showed leaks from sewer and wastewater infrastructure were significant sources of bacteria pollution in the French Broad Watershed. The six-month sewer system overflow data from DEQ underscores those findings and supports part of MountainTrue’s policy agenda: reducing human-derived bacteria contamination by fixing our broken sewer and wastewater systems.
“The French Broad River is a significant public resource and a linchpin for our local economy” explains Hartwell Carson. “Protecting it will require action on the part of elected officials and agency personnel at all levels of government. Through our iloverivers.org advocacy campaign, we succeeded in getting the City of Asheville to participate in a Storm Water Taskforce. In the General Assembly, we’re advocating for targeted clean water investments to be included in this years budget, such as $3 million for septic system and wastewater upgrades through the Community Conservation Assistance Program, and $26 million to help farmers keep cattle and stormwater runoff out of our rivers through the Agricultural Cost Share Program and the Agricultural Water Resource Assistance Program. In Congress, we’re calling on our delegation to support the $111 billion in the American Jobs Plan that is allocated for water infrastructure.”
The public can read more about the issues affecting water quality, and advocate for the policies and reforms needed to fix them at iloverivers.org.