Take Action: Ask the Town of Woodfin To Support A Ban On Single-Use Plastic Bags
Take Action: Ask the Town of Woodfin To Support A Ban On Single-Use Plastic Bags
We need you to take action to help pass a common-sense law to reduce plastic pollution in Buncombe County. The first step is getting the Town of Woodfin to pass a resolution of support.
Please email your local lawmakers and let them know you support a ban on single-use plastics.
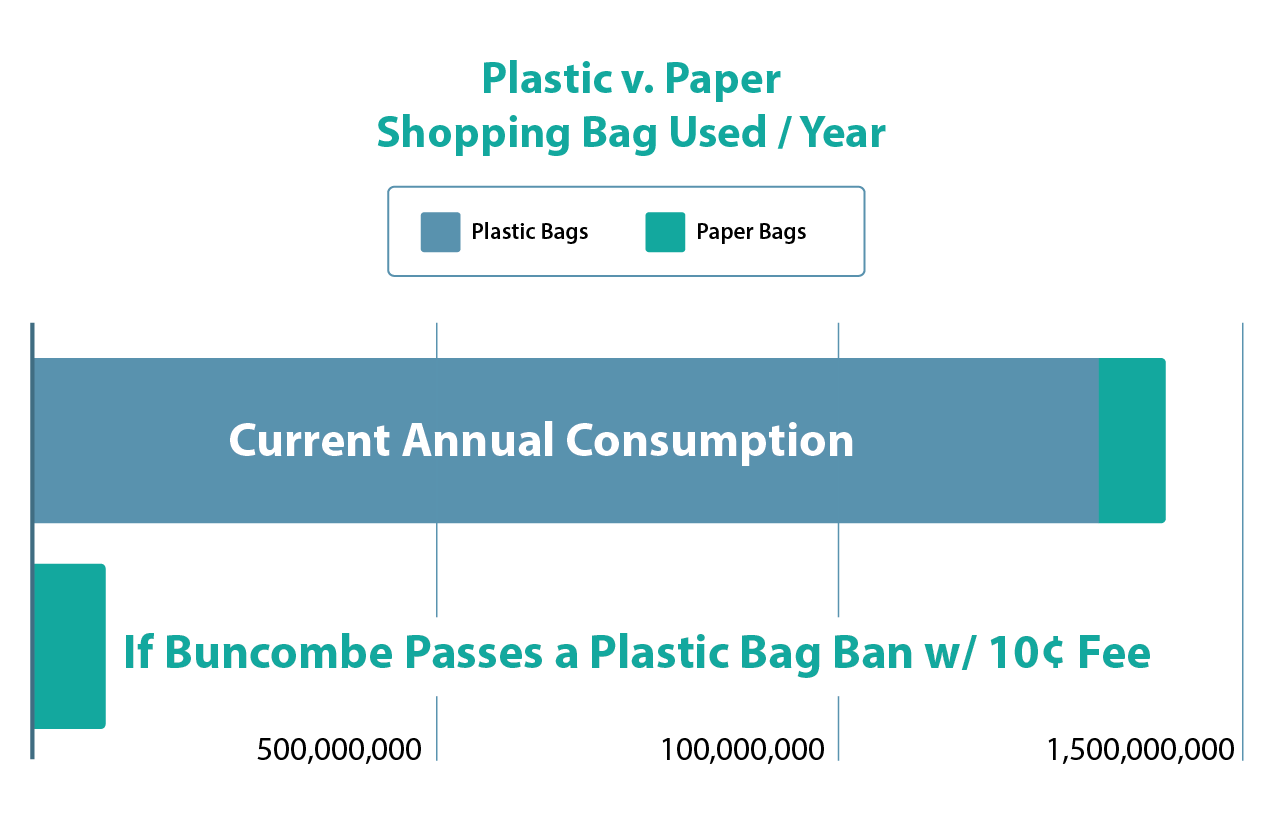
Plastic pollution is a global problem, and we must act locally to do our part. That’s why MountainTrue is advocating for a county-wide ban on single-use plastic bags and styrofoam at grocery and retail store checkout counters paired with a 10-cent fee on paper bags.
More than 500 local governments in 28 states across the country have already passed such laws to reduce plastic pollution. If we want Buncombe County to be next, we need to show them that we have broad support.
So why are we asking you to email the Mayor and Councilpersons of the Town of Woodfin? As part of a broader multi-pronged strategy, we’re encouraging towns and cities to pass resolutions supporting such a law, which we hope will encourage our Buncombe County Commissioners to act.
To the best of our knowledge, these town officials do not oppose a ban on plastic bags. Many of the officials that we’ve spoken to are enthusiastically supportive. That’s why it’s essential that we communicate with them positively and respectfully.
Facts About Our Ban on Single-Use Plastics
Microplastics are a dangerous emerging contaminant.
Plastics don’t biodegrade; they break down into smaller and smaller pieces of microplastic that stay in our environment for thousands of years.
These microscopic pieces of plastic waste are everywhere.
We all breathe/consume approximately one credit card’s worth of microplastics every week. Microplastics have been found in the human placenta and breast milk.
Plastic production generates as much CO2e (carbon dioxide equivalent) gas as 116 coal-fired power plants.
As of 2020, the US plastics industry was responsible for at least 232 million tons of CO2e gas emissions per year, which is the equivalent of 116 average-sized (500-megawatt) coal-fired power plants (Beyond Plastics: The New Coal: Plastics and Climate Change, 2021).
Plastic production is ramping up and much of it is for the purpose of creating wasteful, single-use plastics.
42% of plastic production is for single-use packaging (Science Advances: Production, Use, and Fate of All Plastic Ever Made, 2017). Half of all plastics created were produced in the last 15 years (NRDC: Single-Use Plastic 101, 2020).
Plastic films account for 40% of the microplastics found in the French Broad River.
MountainTrue has conducted widespread microplastic sampling throughout the French Broad Watershed. On average, we’ve found 15.5 pieces of microplastic per 1-liter sample of water, with some samples as high as 40 or 50 pieces per liter. The most common type of microplastics in the French Broad River is films (39.5%), the sources of which are plastic bags, food packaging, and candy wrappers.
Plastics are harmful to human health.
Plastics contain 7% chemical additives on average. Researchers suspect these chemicals contribute to reproductive health problems and declining sperm counts in Western countries. Phthalates, used to enhance the durability of plastic products, are found in personal care products, food packaging, children’s toys, shower curtains, and more. These chemical additives disrupt the endocrine system and harm the reproductive and nervous systems.
Styrofoam contains a likely carcinogen that leaches into food, drinks, and water supplies.
Styrene is used to make styrofoam cups, food containers, and disposable coolers, and leaches into the food and drinks they hold and from landfills into drinking water. It’s classified as a likely human carcinogen that causes liver, kidney, and circulatory problems.
A ban on single-use plastic bags in Buncombe County would have significant environmental benefits.
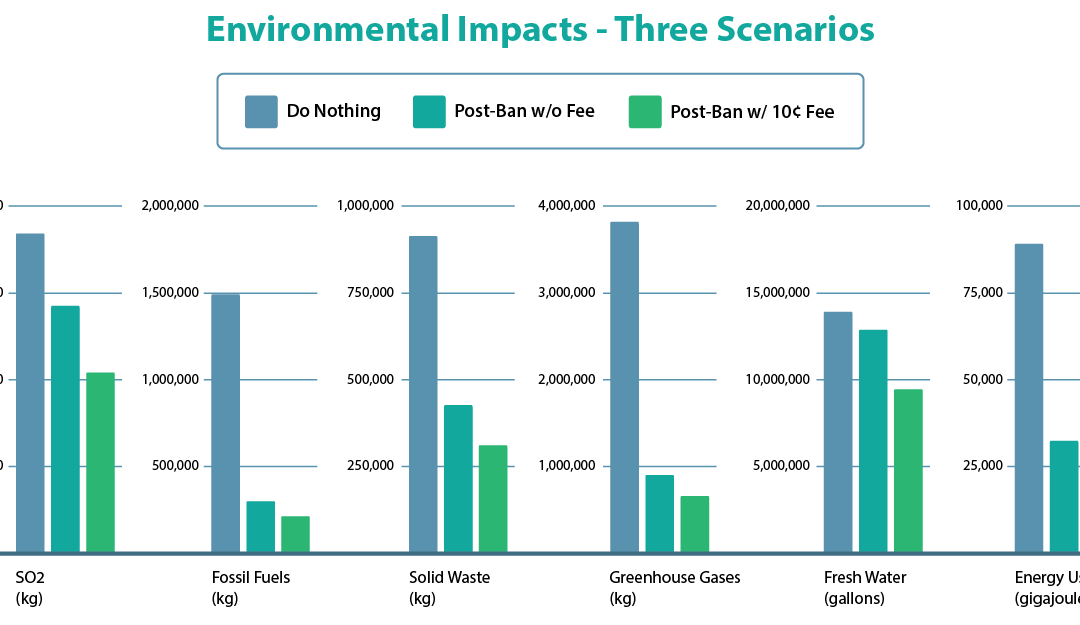
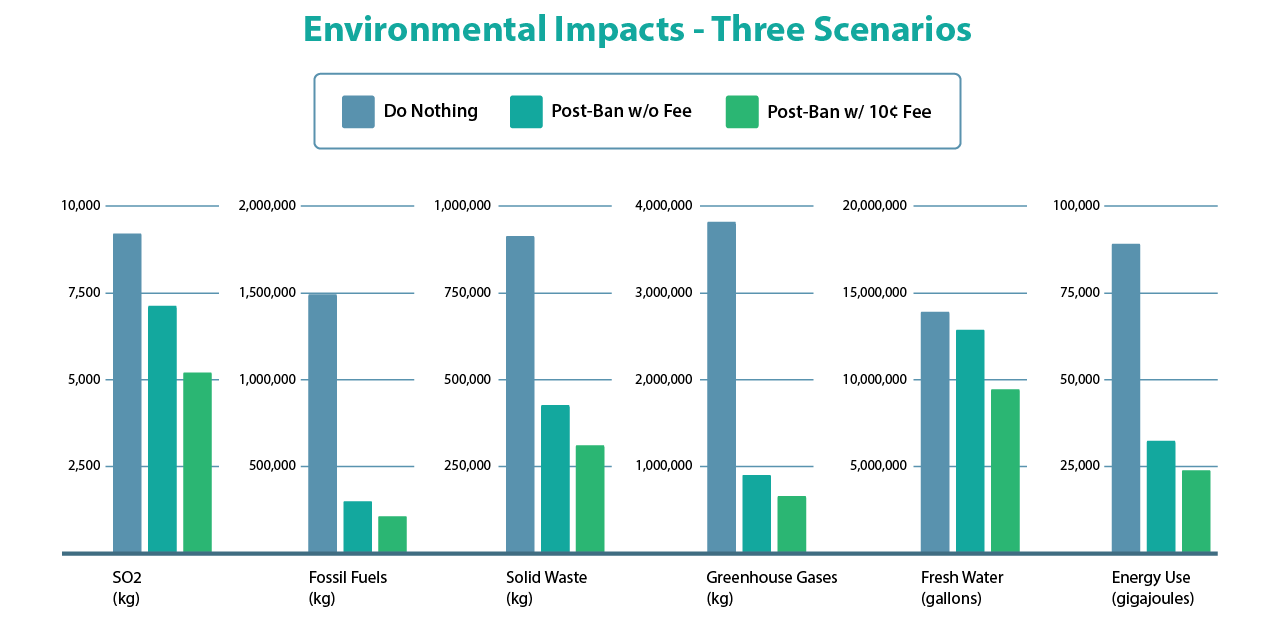
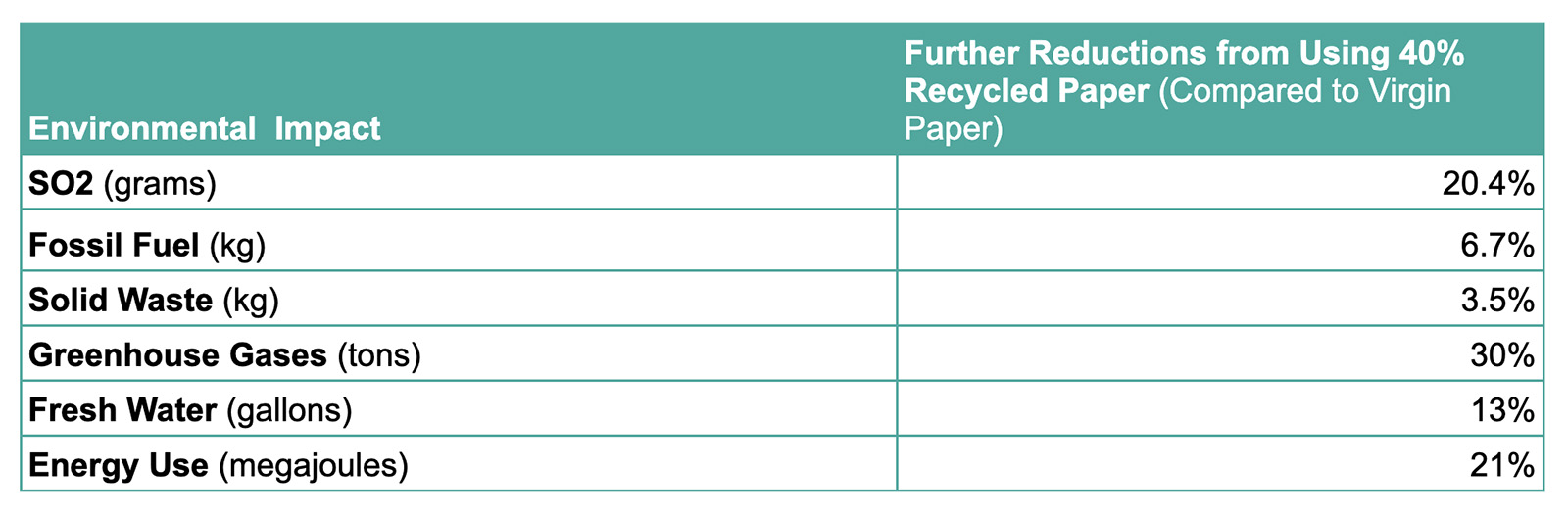
A ban on single-use plastic bags paired with a 10-cent fee on paper bags would reduce Sulfur dioxide (SO2) emissions by 43%, fossil fuel consumption by 86%, solid waste by 66%, greenhouse gas emissions by 83%, fresh water consumption by 32%, and energy use by 73.3% compared to plastic. Read more about the environmental benefits of our proposed ordinance here.
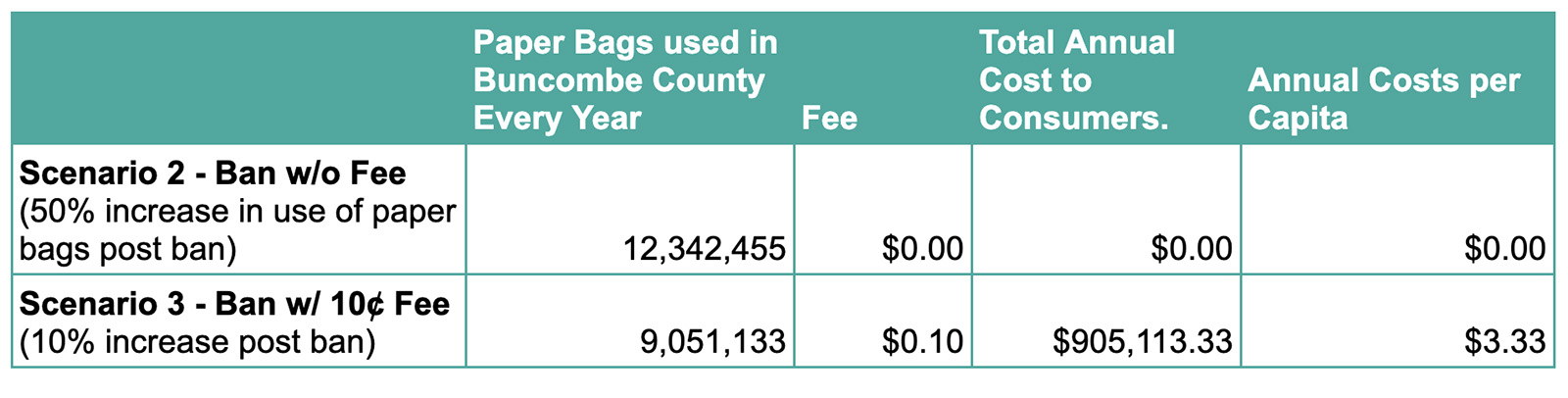
Our plastic bag ban would not be overly burdensome for people with lower incomes.
Our proposed ordinance would exempt customers using EBT, SNAP, and WIC from paying the 10-cent fee on paper bags. Even without that exception, the average cost to Buncombe County consumers would only be $3.33 per year, and customers can reduce or eliminate those costs by bringing reusable bags to the store.
Buncombe County has the legal authority to pass a plastic bag ban under the North Carolina Solid Waste Management Act.
The NC Solid Waste Management Act asserts that it’s North Carolina’s policy to prioritize waste reduction at the source and mandates that towns, cities, and counties implement programs and other actions to address deficiencies and “protect human health and the environment.” Because the presence of a pollutant that is harmful to human health and the environment has been documented in our region, the law mandates that local governments act.