
Help Make the Pigeon River Healthier
Help Make the Pigeon River Healthier
Action Expired
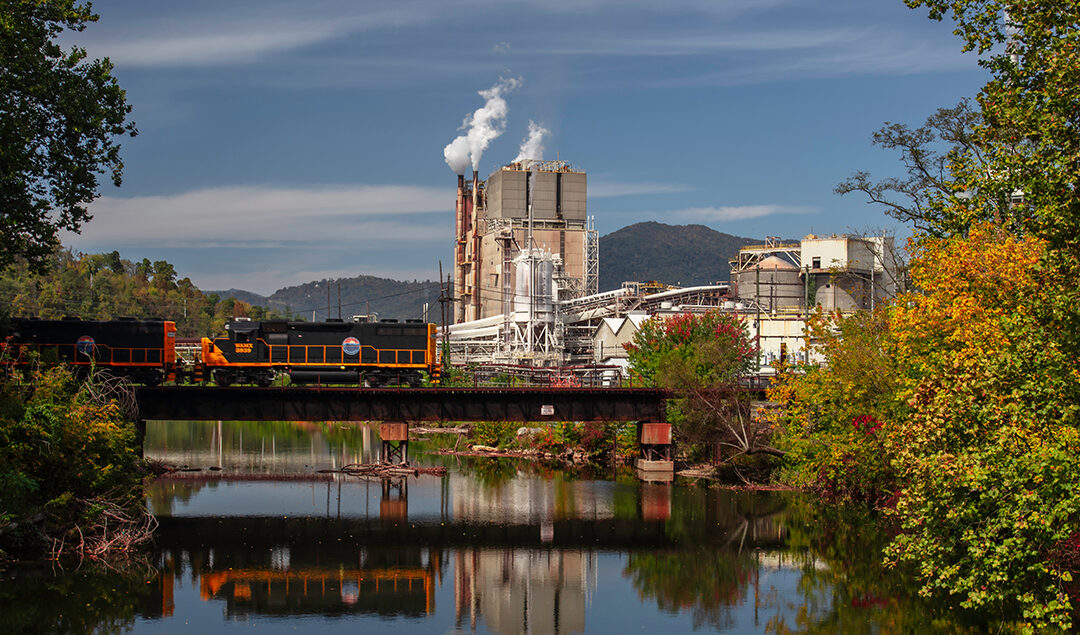
Blue Ridge Paper Products has a long history on the Pigeon River in Canton. It has provided good quality jobs for decades, but also caused significant environmental impacts to the Pigeon River. Because of the pressure brought to bear from the public, environmental groups and the EPA, significant improvements in the amount and quality of the discharge to the river have been obtained, but we have a long way to go.
The goals of the Clean Water Act are to have all waters be fishable and swimmable. The way that regulators have tried to achieve those goals while balancing the interests and needs of industry is by slowly reducing permit discharge limits over time. The draft permit as proposed by the Department of Environmental Quality (DEQ) takes a step backwards by weakening regulations, requiring less monitoring and allowing for more pollution to be discharged to the river.We are calling on the public to make their voice heard for continued improvements at the mill, so the Pigeon River can finally meet the goals of the Clean Water Act, almost 50 years after its passage. Attend and speak at the public hearing and submit comments to DEQ.Update: The NC Department of Environmental Quality (DEQ) is postponing the public hearing until April 14 and extending the period for public comments until April 30.
What you can do
-
- Provide Public Comment via email to the Department of Environmental Quality.
The public comment period has been extended until April 30. Take action today. - Speak up at the online public hearing:
You must register by noon on April 14. Click here for registration and hearing details.
Resources
- The draft wastewater permit and all related documents
- Fact sheet for NPDES Permit NC0000272
- Draft permit for Blue Ridge Paper Products LLC. d/b/a Evergreen Packaging
Talking Points
Temperature: Over 8,500 fish were killed in the summer of 2007 from an extremely hot discharge from the paper mill. This hot water discharge did not violate the temperature permit limits at the mill, because their limits during that time relied on a monthly average, which allows wild swings in the temperature of the discharge, and potential fish kills. Data from the NC Wildlife Resources Commission shows a substantial impact of aquatic life between up and downstream monitoring, and temperature is a likely factor in the reduced diversity and abundance of aquatic life downstream of the mill. MountainTrue, with the help of SELC and Clean Water for NC fought and won weekly monitoring limits in the last permit cycle, but those limits are being rolled back to a monthly average. We believe daily monitoring and a daily average limit for temperature is critical to understanding and protecting the Pigeon River. Now is not the time to roll back protections for the river!
- Provide Public Comment via email to the Department of Environmental Quality.
Dioxin: Reduction in dioxin fish monitoring in the draft permit is being proposed. Current monitoring requires monitoring 3 times in 5 years, but the new draft permit reduces that to once every 5 years. This is problematic for two reasons. The most recent sampling conducted in 2014 still shows dioxin in fish tissue, and therefore monitoring on at least the same schedule should be continued until dioxin is no longer present in fish tissue samples. Secondly, the permit renewal cycle is many years overdue, the last fish tissue sample was taken over six years ago. That means, if new sampling is conducted only once in the next five years, that could mean that we only have one sample in 11 years. For these reasons we call on DEQ to continue the same sampling schedule of three times within every five years.
Fecal Coliform: The mill not only processes its own waste, but also serves as a wastewater treatment plant for the town of Canton. Violations for fecal coliform have been frequent in the last decade with MountainTrue documenting at least 25 permit violations, sometimes in excess of 250 times the safe limit for fecal coliform. The Mill has also commonly violated its permitted standards for total suspended solids and biological oxygen demand. There is an urgent need for significant improvements to the wastewater treatment plant to ensure the river and downstream river recreation users are protected from harmful and dangerous levels of bacteria in the river.
- Chloroform: DEQ is proposing to allow the mill to increase their discharge of chloroform, a possible carcinogen. This is to an internal discharge point, so we need additional information to determine how much of this discharge is reaching the Pigeon River. The goal of the Clean Water Act is to reduce pollution discharges until all waters are fishable and swimmable. In this instance, not only is the discharge not decreasing, but the mill will be allowed to discharge even more cancer causing chemicals into the Pigeon River. The 2010 permit allowed for chloroform discharge allowances of 5.1 lb/day (as monthly average) or 8.6 lb/day (daily maximum). The 2021 proposed permit ups those limits to 6.27 lb/day (as a monthly average) and 10.5 lb/day (daily maximum). DEQ should be reducing those allowance, not letting the papermill pollute more.
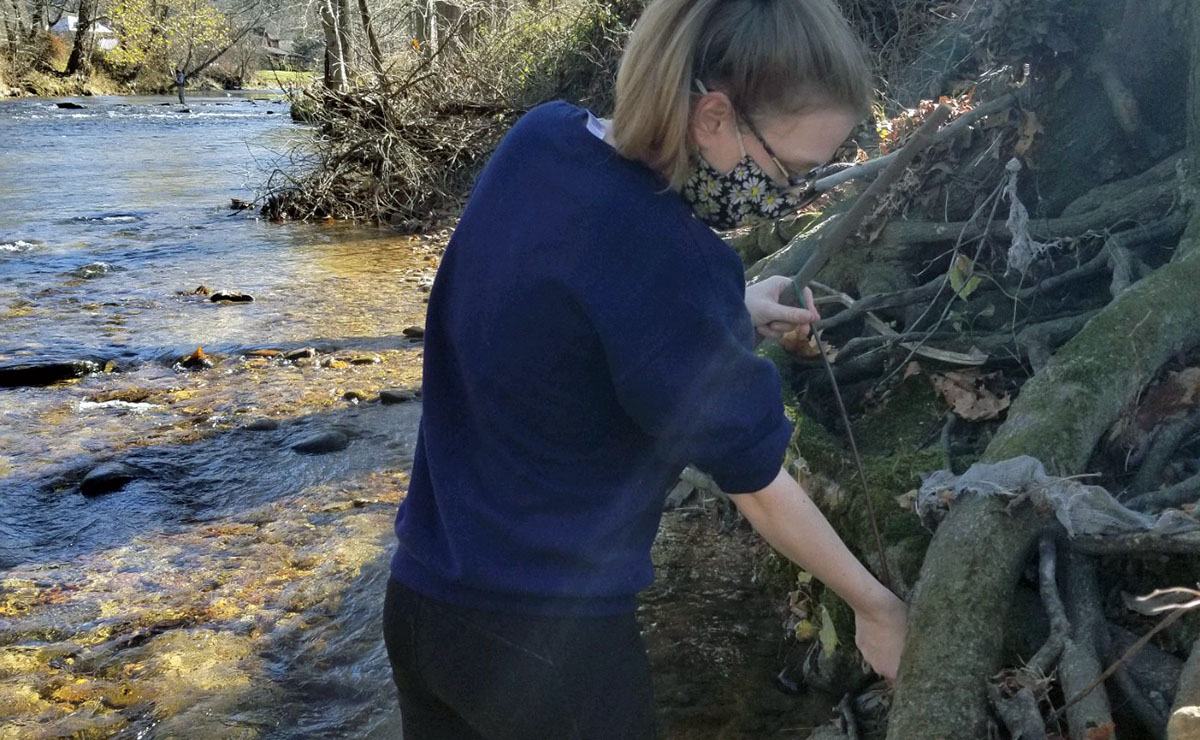























 Live staking volunteers plant live cuttings of trees and shrubs to reduce sediment pollution.
Live staking volunteers plant live cuttings of trees and shrubs to reduce sediment pollution.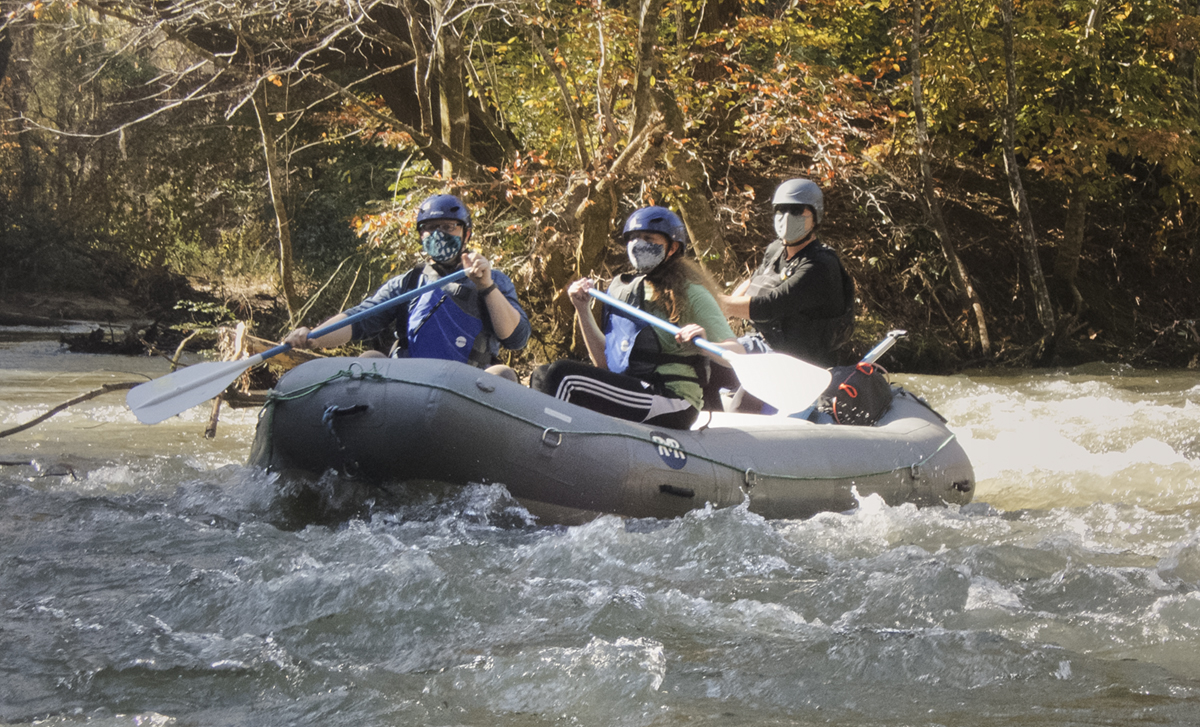 The experienced paddlers of the PHHAT team head down the Green River to treat hemlock trees.
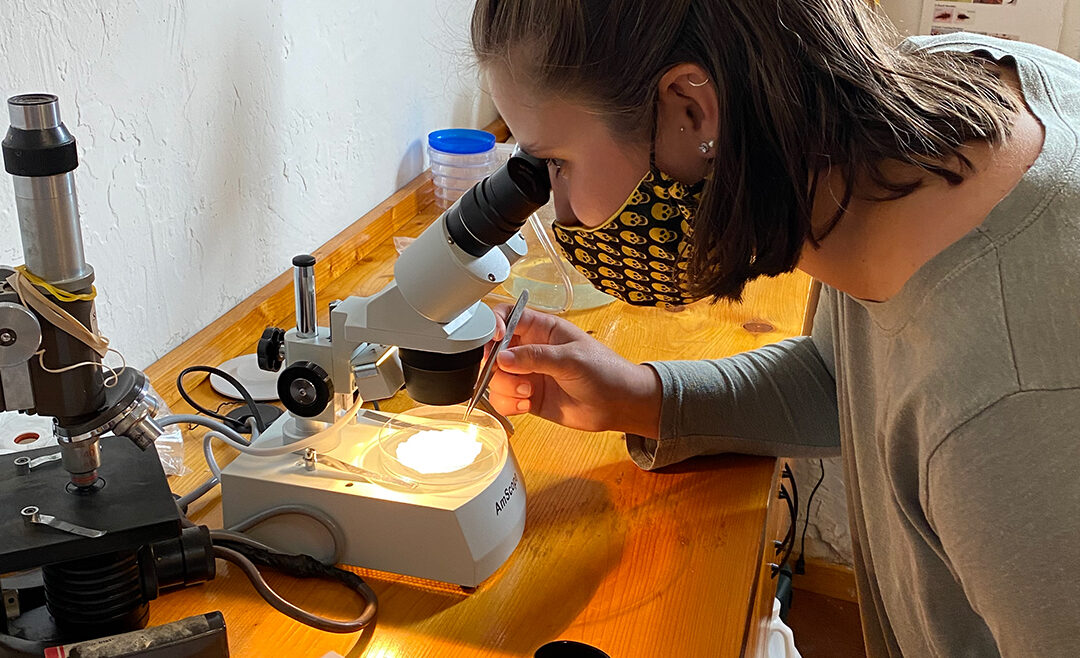
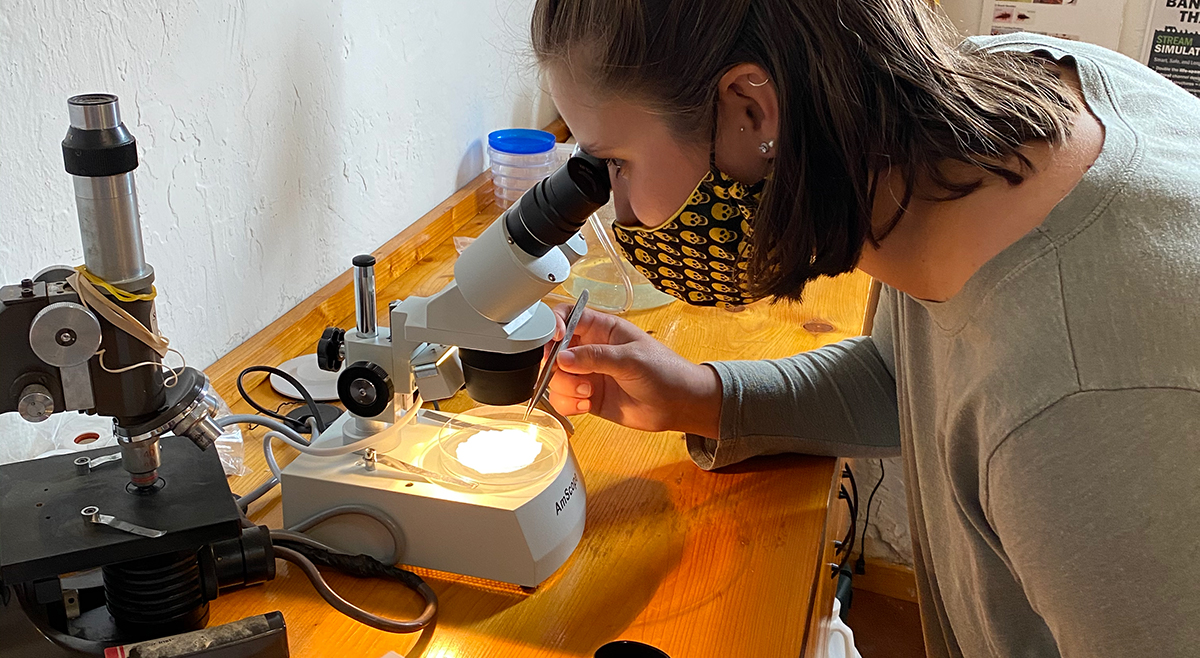
The experienced paddlers of the PHHAT team head down the Green River to treat hemlock trees.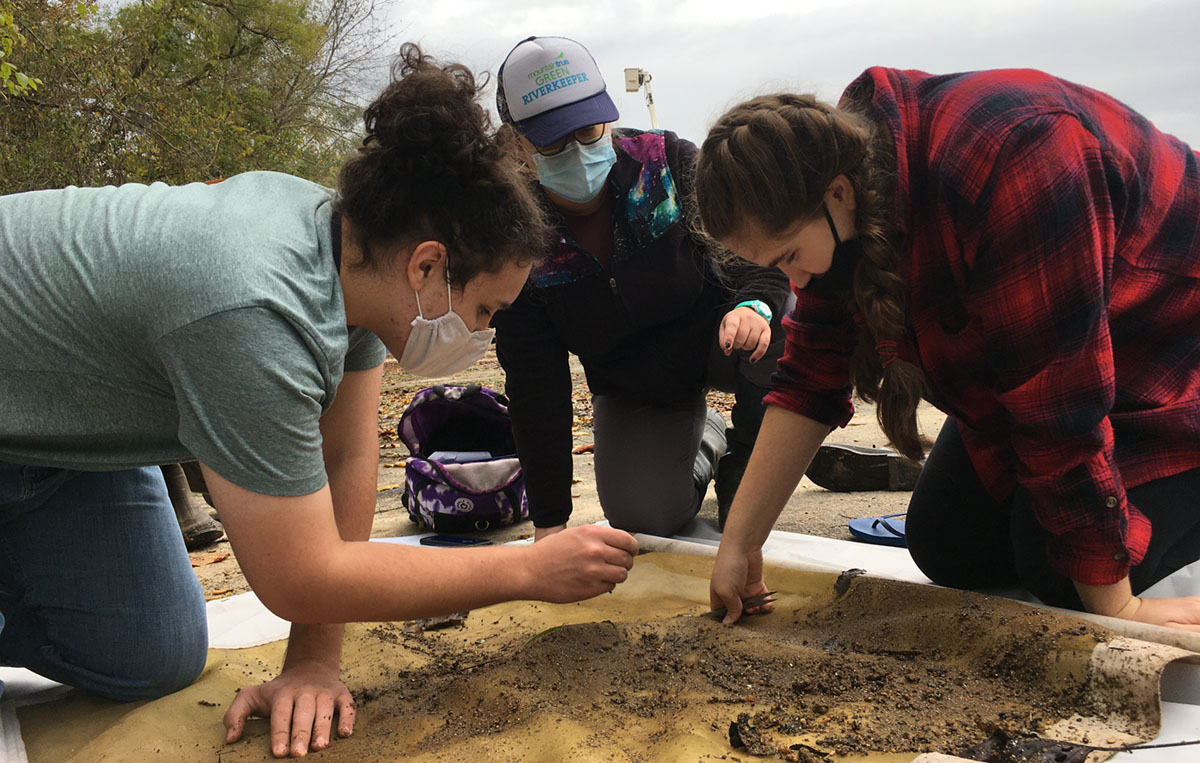 SMIE volunteers inspect water bugs to gauge the health of our rivers and streams.
SMIE volunteers inspect water bugs to gauge the health of our rivers and streams. Longtime cleanup participant Benjamin Davis won the prize for most creative photo from this year’s cleanup!
Longtime cleanup participant Benjamin Davis won the prize for most creative photo from this year’s cleanup!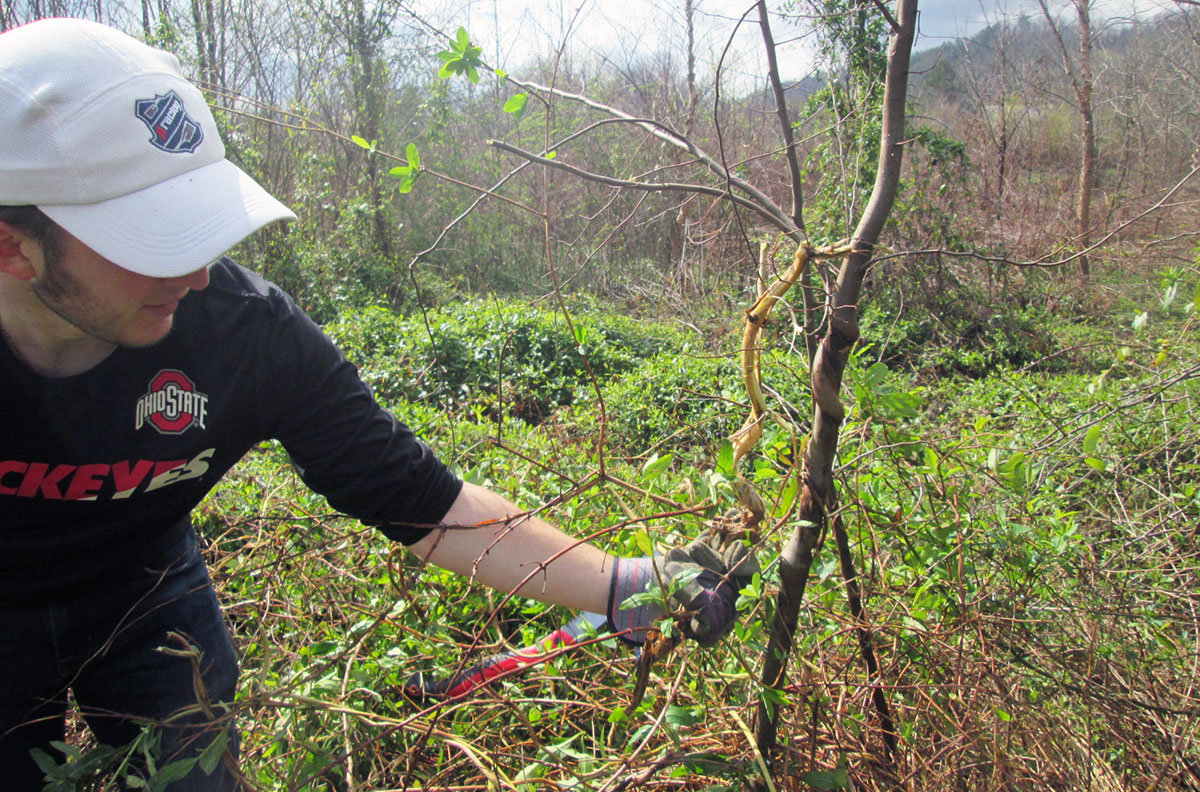 Photo caption: Severing vines of kudzu, oriental bittersweet and honeysuckle is the first step to controlling non-native invasive plants at Island Park.
Photo caption: Severing vines of kudzu, oriental bittersweet and honeysuckle is the first step to controlling non-native invasive plants at Island Park.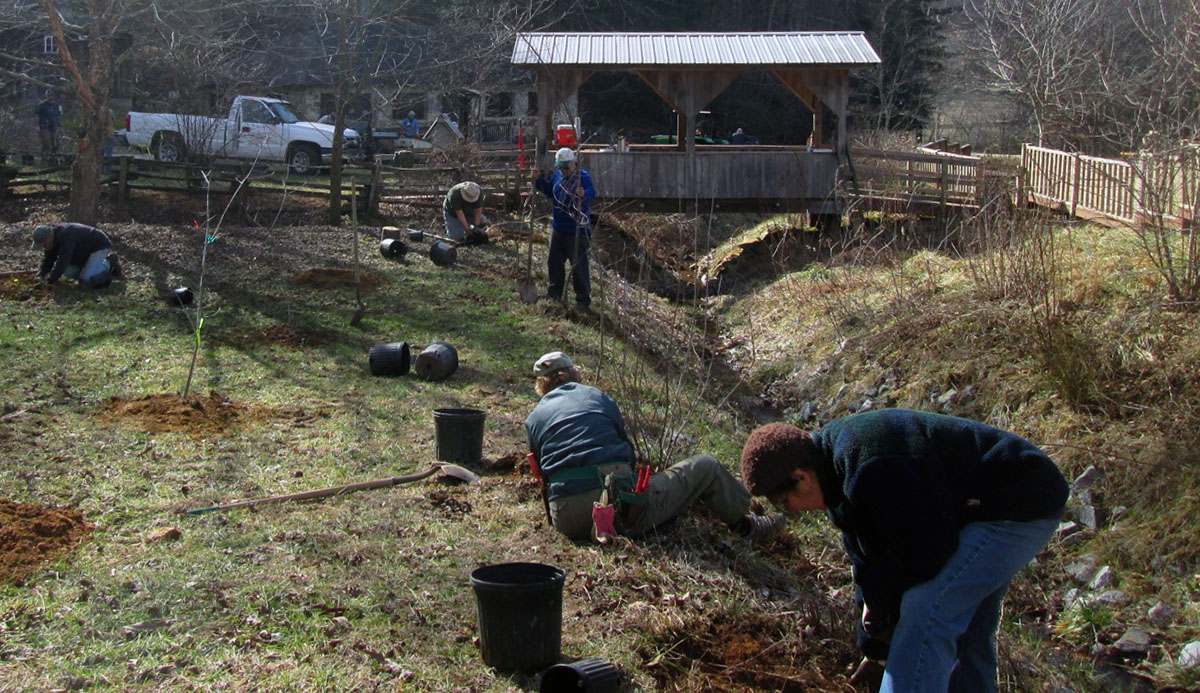 Volunteers plant native trees and shrubs along a small stream at the Georgia Mountain Research & Education Center in January 2019.
Volunteers plant native trees and shrubs along a small stream at the Georgia Mountain Research & Education Center in January 2019.